Security Testing
Tomaso Vasella

When I started virtualizing production environment in 2002/2003 many people didn’t trust the technology and (to be honest) they didn’t understand the technology either. So I had to make big efforts in explaining the advantages of a virtual environment and the best of all arguments was to show them how it worked. Well, I guess I don’t have to explain it here anymore.
Still, when it comes to security, there are some more concerns providing a virtual environment. Let’s take a view on the following picture:
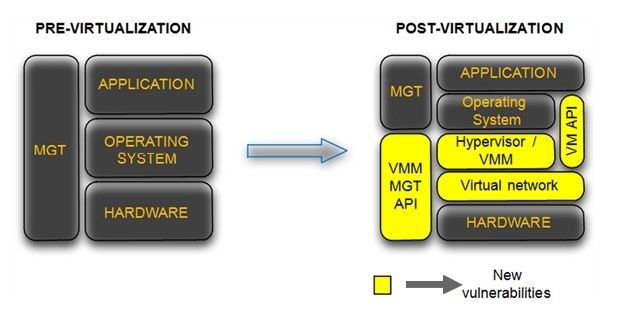
As we can see virtualization is adding a new layer that is susceptible to a new way of attacks and exploitation (after all it’s more software code and we all know what it means…) and we need to be aware of it and take the needed precautions as we always should do. This discussion becomes more important when is comes to high risk environments like in a DMZ.
I’m not going to into the details of the security design of a virtual environment as it really depends on the goals you need to achieve.
Also I’m not talking about the security requirements of the virtual systems OS, this is out of scope, we’ll only talk about the underlying virtual environment. Although a secured operating system is a prerequisite in our case, there are plenty of guidelines on how to achieve this.
What I like to point here are the recommended security requirements for a virtual infrastructure architecture as schematic represented in the following picture:
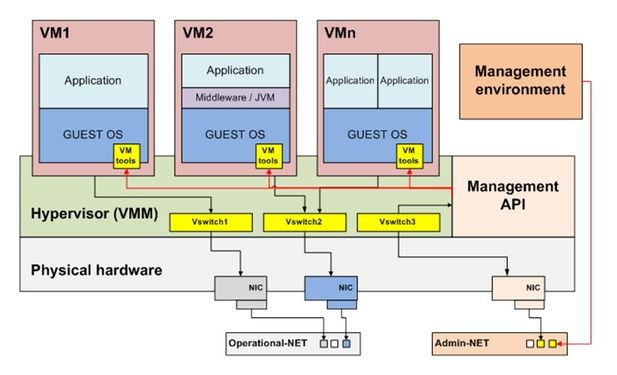
We need to take particular care on the new administration environment and on the virtual network layer. As already suggested in the picture one recommendation is clear:
use an isolated administration environment
Managing several machines form a central site with special administration paths, makes the administration environment a clear target for attacks – Why should I attack several different systems when I can get it all at once? Therefore this is probably the best point to start in securing your environment. Make sure you also:
Now let’s take a look a the virtual environments new attack areas as shown in the following picture:
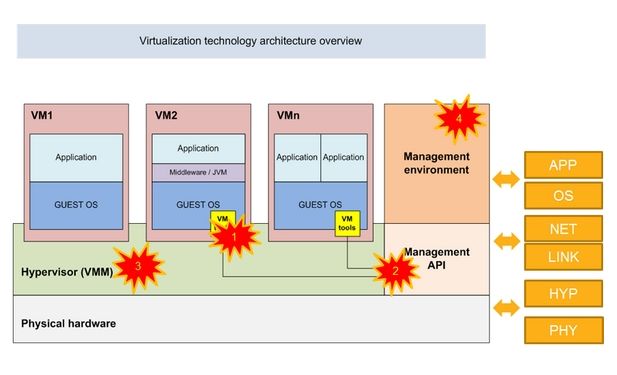
| Area | Components | Attack |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VMtools (Client management API) | VM jumping, guest hopping or Hypervisor DoS Attacks |
| 2 | VM management (Host management API) | Hypervisor DoS |
| 3 | Hypervisor (Virtual Machine Monitor) | Hypervisor escape, Management privilege escalation |
| 4 | VM management infrastructure | Management tools unauthorized access, privilege escalation & DoS |
Attack areas 1 to 3 are not so common, but the attacks on the administration infrastructure are well known and use the already known paths. This leads to the next recommendation:
keep your virtual environment up to date (including the management infrastructure)
It is crucial to keep those environment patched and if not possible: Implement workarounds (e.g. strict configuration settings) to lower the risk to an acceptable level.
Particular attention on security requirement is needed in the DMZ (or higher risk) environments where following recommendation are a must:
Of course those requirements make sense in every ICT environment, not only in the virtual ones.
Now to bring some practical knowledge I’ll publish a VMware baseline excerpt that would make sense in our virtualized DMZ environment.
| Hypervisor | ||
|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Description | Value |
| VirtualCenter.VimPasswordExpirationInDays | Ensure that vpxuser auto-password change meets policy | 90 days |
| Configure the ESXi host firewall to restrict access to services running on the host | – | site specific |
| Configure NTP time synchronization | /etc/ntp.conf | site specific |
| Ensure proper SNMP configuration | /etc/vmware/snmp.xml | site specific |
| Do not use default self-signed certificates for ESXi communication | – | – |
| Disable DCUI to prevent local administrative control | – | stopped |
| Disable ESXi Shell unless needed for diagnostics or troubleshooting | – | stopped |
| Disable SSH | – | stopped |
| Enable lockdown mode to restrict remote access | – | enabled |
| Verify no unauthorized kernel modules are loaded on the host | – | – |
| Configure persistent logging for all ESXi host | Syslog.global.logDir | log directory |
| Configure remote logging for ESXi hosts | Syslog.global.logHost | syslog-server |
| Zero out VMDK files prior to deletion | – | – |
| Virtual Machines (VMtools) | ||
| Parameter | Description | Value |
| Generic | For directly accessed VM systems like DNS, SMTP & WEB server don’t install VMtools at all. | – |
| vmci0.unrestricted | Disable VM-to-VM communication through VMCI | false |
| RemoteDisplay.maxConnections | Limit sharing of console connections | 2 |
| floppyX.present | Disconnect unauthorized devices | false |
| ideX:Y.present | Disconnect unauthorized devices | false |
| parallelX.present | Disconnect unauthorized devices | false |
| serialX.present | Disconnect unauthorized devices | false |
| usb.present | Disconnect unauthorized devices | false |
| isolation.device.connectable.disable | Prevent unauthorized removal, connection and modification of devices. | true |
| isolation.device.edit.disable | Prevent unauthorized removal, connection and modification of devices. | true |
| isolation.tools.copy.disable | Explicitly disable copy/paste operations | true |
| isolation.tools.dnd.disable | Explicitly disable copy/paste operations | true |
| isolation.tools.setGUIOptions.enable | Explicitly disable copy/paste operations | false |
| isolation.tools.paste.disable | Explicitly disable copy/paste operations | true |
| isolation.tools.ghi.autologon.disable | Disable certain unexposed features | true |
| isolation.bios.bbs.disable | Disable certain unexposed features | true |
| isolation.tools.getCreds.disable | Disable certain unexposed features | true |
| isolation.tools.ghi.launchmenu.change | Disable certain unexposed features | true |
| isolation.tools.memSchedFakeSampleStats.disable | Disable certain unexposed features | true |
| isolation.tools.ghi.protocolhandler.info.disable | Disable certain unexposed features | true |
| isolation.ghi.host.shellAction.disable | Disable certain unexposed features | true |
| isolation.tools.unity.disable | Disable certain unexposed features | true |
| isolation.tools.unityInterlockOperation.disable | Disable certain unexposed features | true |
| isolation.tools.unity.taskbar.disable | Disable certain unexposed features | true |
| isolation.tools.unityActive.disable | Disable certain unexposed features | true |
| isolation.tools.unity.windowContents.disable | Disable certain unexposed features | true |
| isolation.tools.unity.push.update.disable | Disable certain unexposed features | true |
| isolation.tools.vmxDnDVersionGet.disable | Disable certain unexposed features | true |
| isolation.tools.guestDnDVersionSet.disable | Disable certain unexposed features | true |
| isolation.tools.autoInstall.disable | Disable tools auto install | true |
| isolation.tools.vixMessage.disable | Disable VIX messages from the VM | true |
| Virtual Network | ||
| Parameter | Description | Value |
| isolate-mgt-network-vlan | Ensure that vSphere management traffic is on a restricted network | – |
| isolate-storage-network-vlan | Ensure that IP-based storage traffic is isolated | – |
| isolate-vmotion-network-vlan | Ensure that vMotion traffic is isolated | – |
| no-unused-dvports | Ensure that there are no unused ports on a distributed virtual port group | – |
| reject-forged-transmit-dvportgroup | Ensure that the Forged Transmits policy is set to reject. | reject |
| mac-change-dvportgroup | Ensure that the MAC Address Change policy is set to reject | reject |
| promiscuous-mode-dvportgroup | Ensure that the Promiscuous Mode policy is set to reject | reject |
| no-native-vlan-1 | Ensure that port groups are not configured to the value of the native VLAN | – |
| no-reserved-vlans | Ensure that port groups are not configured to VLAN values reserved by upstream physical switches | – |
| no-vgt-vlan-4095 | Ensure that port groups are not configured to VLAN 4095 except for Virtual Guest Tagging (VGT) | – |
| verify-vlan-id | Ensure that all virtual switch VLAN’s are fully documented and have all required and only required VLANs | – |
| vswitcht-forged-transmit | Ensure that the Forged Transmits policy is set to reject | reject |
| vswitch-mac-changes | Ensure that the MAC Address Change policy is set to reject | reject |
| vswitch-promiscuous-mode | Ensure that the Promiscuous Mode policy is set to reject | reject |
Applying to those recommendation and remembering that security is a process and every control should be monitored and verified, you should have no bigger risk in providing a virtualized DMZ environment.
Our experts will get in contact with you!

Tomaso Vasella

Eric Maurer

Marius Elmiger

Eric Maurer
Our experts will get in contact with you!