Security Testing
Tomaso Vasella

Wearables analyse everything. Pulse, sleep, breathing, distance. To achieve this, they don’t just use new technology and proprietary sensor technology. Established technology is being repurposed and still used. Let’s have a look under the hood of Google Glass, Jawbone Up and their kin.
In order to analyse the recorded data on the fly, Wearables are in steady wireless communication – Nike FuelBand, Google Glass and OM Signal Shirt among them – with other devices. Some have an additional port where a regular USB-cable can be plugged in. A few use other means of connection, such as the Jawbone Up. It has a 3.5mm audio jack, a regular plug used to connect headphones.
To communicate wirelessly, most products use Bluetooth or the less energy-consuming version Bluetooth Low Energy. In some devices, those aiming to record sportive progress, ANT and ANT+ are used. It’s not unreasonable to entertain WLAN as a means of connection, even though it uses more power than the other signals.
Bluetooth is a wireless protocol, developed and specialized by the Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG) to which over 20000 companies belong. Using Bluetooth, users can create Wireless Personal Area Networks (WPAN). Those are wireless networks that only span about a 30 Meter radius.
Bluetooth broadcasts on the 2.4GHz ISM Band, which stands for Industrial, Scientific, Medical. The ISM-Band is a license free frequency band that is also used by WLAN, ANT as well as microwave ovens and cordless phones. Due to the vast amount of devices broadcasting on this frequency, interferences are frequent. To avoid data collisions as much as possible, Bluetooth-devices change their broadcast channel up to 1600 times per second.
The security features are very distinct from protocol version to protocol version. The main specification kept three things in mind:
According to Bluetooth Core Specification v4.1 there are four modes of encryption:
| Modus | Description | Details |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Non-Secure | Doesn’t initiate any security features. |
| 2. | Service Level Enforced Security | Defines that the security features are initiated after the successful establishment of the connection. They can vary from service to service(Authorization, Authentication, Encryption) |
| 3. | Link Level Enforced Security | The security features are initiated before the connection is complete. Therefore, all services running on this connection are equally protected (Authentication, Encryption) |
| 4. | Service Level Enforced Security | Similar to the 2nd mode, the security features are initiated after the successful establishment of the connection. The security requirements can be adapted. Therefore, there are different levels, including a level that has no security features for service-discovery traffic. This allows for a more flexible definition of security features. |
Bluetooth Low Energy, also known as Bluetooth Smart, is an extension of the existing Bluetooth Standard that was first implemented in the smartphones iPhone 4s, Google Nexus 4 and Samsung Galaxy SIII. It’s a more energy-efficient version of Bluetooth. This, however, had effects on security, so the connecting of devices was simplified. Also, the host is now responsible for key generation. The encryption itself is happening in the controller. In devices like Jawbone Up, this is a chip worn inside the wrist-mounted device.
Bluetooth Low Energy uses the Advanced Encryption Standard – Counter with CBC-MAC (AES-CCM)Cipher that is also used in WLAN Encryption WPA2 and is compliant with FIPS-140 requirements, released by the National Institute of Technology (NIST). NIST is the name of a US-standardizing agency that releases advisories and standards for other branches of the US government. They are also used by many companies worldwide.
Another protocol, interesting in particular for Wearables, is ANT/ANT+. Using smaller frequency channels, data modulation consumes less energy. This leads to longer battery life. Battery life is the main problem that still causes developers some headache. The criticism of Samsung Galaxy Gear included the lack of battery life which just might have cost the device its popularity.
ANT is being developed by Dynastream Innovations Inc. and is being used in all mobile phones built by Samsung and Sony. Like all non-licensed radio technology, ANT is operating on the 2.4GHz ISM-Band. ANT+ is an extension of ANT that seeks to enable interoperability between ANT devices that were manufactured by different companies.
The developers of the ANT Protocol divided the functionality of an ANT system into three layers. The following graphic, taken from the documentation of an ANT+ chip shows, how the three layers are mapped to the well-established OSI model that has seven layers. From this, it becomes apparent that the functionality of the encryption was meant to happen in the layer User Defined. Said layer is mapped to three OSI layers and could be referred to as the application layer of ANT.
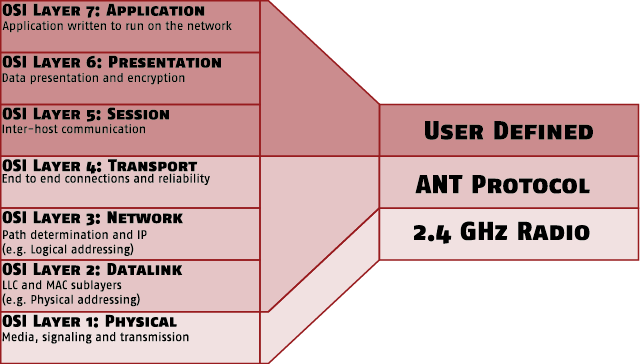
In the technical FAQ of ANT there’s mention of ANT using only an 8 byte network key. So in order to join an ANT network you need an 8 bit network number and said key. From this, we can deduct the following math: (8 Bit + 8 * 8 Bit)2 = 5184 different possible network configurations. The effort to detect the correct combination of number and key using brute force wouldn’t take much time at all. ANT offers ANT-FS (ANT File Share) which can be used to share data via ANT and also encrypt it.
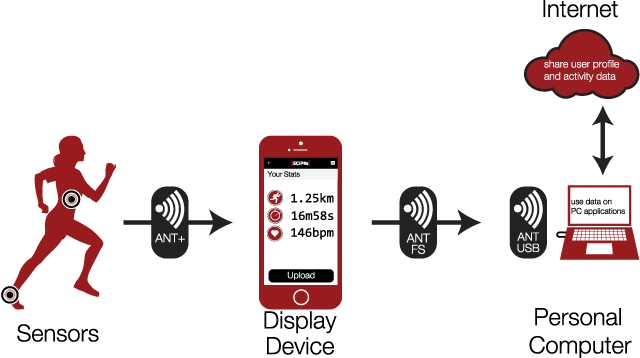
Which encryption is being used is not stated in ANT-FS’s specifications. In the tech specs of an ANT chip manufactured by Texas Instruments, however, there is mention of an AES-128 Bit encryption. So it’s possible that this is the one being used.
Our experts will get in contact with you!

Tomaso Vasella

Eric Maurer

Marius Elmiger

Eric Maurer
Our experts will get in contact with you!